There are many ways to purify water. We thought we would discuss
some of these methods here, to better understand the quality
of the filters we offer.
|
 There are
5 types of water contaminants: There are
5 types of water contaminants:
-
- Biological Entities
-
- Heavy Metals
-
- Organic Chemicals
-
- Inorganic Chemicals
-
- Radioactive Material
|
Steam
Distillation
QUALITY distillation is capable of removing all
FIVE major
categories of water pollution.
Steam distilled water
is produced by a completely natural process:
simple heating and cooling, like earth's natural rain
process, resulting in a product with completely pure
qualities. This is because natural processes are at work in the
distillation system - heat, steam and gravity. Steam
is always produced by the boiling process of
distillation while gravity is always on the job,
separating dissolved solids from the steam.
Carbon filters
(Charcoal)
Many purifier systems use
activated
carbon filters as the first filter, carrying
out the role of a mechanical pre-filter. There are many different grades of
carbon, ranging from granulated activated
carbon (GAC) to premuim ultra compact
activated coconut shell carbon. With some
systems, if this filter is used
to filter out sediments, then iron and even
calcium will plug up the microscopic areas
of adsorption, shortening its effective life
considerably. The carbon filter removes a
host of contaminants such as chlorine,
pesticides, herbicides and other inorganic
materials.
Solid Carbon Block vs.
Loose Carbon
Solid carbon media can often
be subject to “channeling.” Channeling
refers to water passing through least
resistant path of the carbon pores, thus
reducing contact time with carbon. The
result? Your water can pass right through
the solid carbon media on these “familiar,
friendly pathways” with only a minimum of
filtering! Loose Carbon Media, on the
other hand, can be periodically repositioned
by means of a water backwash, or in some
cases by tapping or shaking the filter
medium itself. This means that your water
will not be able to establish those
familiar, friendly pathways that enable it
to pass through your system virtually.
(Solid carbon media makers would
probably disagree.)
more
about carbon filters
Far Infrared Light
One of the reasons FIR has beneficial
results in a variety of illnesses is the
ability of FIR waves to remove toxins,
which
are often at the core of many health
problems. Since humans are bio-accumulators,
numerous toxins, that cannot be removed
immediately after entry, are stored in our
bodies. For example, when toxic gases such
as sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide or toxic
substances such as lead, mercury or chlorine
meet large water molecules, they are
encapsulated by the clusters of water. Where
these toxins are accumulated, blood
circulation is blocked and cellular energy
is impaired.
However, when a 10 micron FIR wave is
applied to these large water molecules, the
water begins to vibrate.
This
vibration reduces the ion bonds of the atoms
which are holding together the molecules of
water. As the breakdown of the water
molecules occurs, encapsulated gases and
other toxic materials are released.
More about
Infrared Light
Ultraviolet
Light
Ultraviolet Light (UV Light) germicidal irradiation has been
studied since the 1930’s and has been used to
destroy the microbes that cause indoor air
and water pollution. For many years, the medical industry
has used UV light to sanitize rooms and
equipment. The Centers for Disease Control
recommend UV lamps for their germicidal effect.
How
Does UV Disinfection Work? UV-C light
deactivates the DNA of bacteria, viruses and
other pathogens, which destroys their ability to
multiply and cause disease. As UV light
penetrates through the cell wall and cytoplasmic
membrane, it causes a molecular rearrangement of
the microorganism's DNA, which prevents it from
reproducing. Specifically, UV-C light
causes damage to the nucleic acid of
microorganisms by forming covalent bonds between
certain adjacent bases in the DNA. The formation
of such bonds prevent the DNA from being
unzipped for replication, and the organism is
unable to reproduce. In fact, when the organism
tries to replicate, it dies.
UV light is MUST for any one with a well.
more about Ultraviolet
Light
|
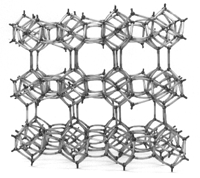 |
- CLINOPTILOLITE
FRAMEWORK MODEL
-
- VIEW
ALONG CLEAVAGE PLANE
-
-
OF CRYSTAL PLATES
|
| |
Zeolites
- Exactly what
are they?
Compositionally, zeolites are similar to clay
minerals. More specifically, both are alumino-silicates.
They differ, however, in their crystalline
structure. Many clays have a layered
crystalline structure (similar to a deck of
cards) and are subject to shrinking and swelling
as water is absorbed and removed between the
layers. In contrast, zeolites have a rigid,
3-dimensional crystalline structure (similar to
a honeycomb) consisting of a network of
interconnected tunnels and cages. Water moves
freely in and out of these pores but the zeolite
framework remains rigid. Another special aspect
of this structure is that the pore and channel
sizes are nearly uniform, allowing the crystal
to act as a molecular sieve. The porous zeolite
is host to water molecules and ions of
potassium and calcium, as well as a variety of
other positively charged ions, but only those of
appropriate molecular size to fit into the pores
are admitted creating the "sieving" property.
Another
important property of zeolite is the ability to
exchange cations. This is the trading of one charged
ion for another on the crystal. One measure of
this property is the cation exchange capacity (CEC).
Zeolites have high CEC's, arising during the
formation of the zeolite from the substitution
of an aluminum ion for a silicon ion in a
portion of the silicate framework (tetrahedral
units that make up the zeolite crystal).
more about zeolites
Ionic Purification
(Ion Exchange)
Ions and Water - Time
for a little chemistry.
Water and the materials
dissolved within it are made up of ions.
Ions are atoms that are
electrically charged and are commonly the
building blocks for other molecules. The
charge may be positive or negative,
depending on the type of ion, with every ion
having a charge which cannot change.
In electrolysis, which involves the use of
two oppositely charged electrodes (negative
and positive) to separate out ions in a
solution, the positive electrode is called
the anode and the negative electrode is
called the cathode. Consequently, negatively
charged ions are attracted to the positively
charged anode (and are therefore called
anions), where as the positively charged cations are attracted to the negative
cathode.
Anions
are negatively
charged ions, formed
when an atom gains
electrons in a
reaction. Anions are
negatively charged
because there are
more electrons
associated with them
than there are
protons in their
nuclei.
Cations
are positively
charged ions, formed
when an atom loses
electrons in a
reaction. Cations
are the opposite of
anions, since
cations have fewer
electrons than
protons.
|
For example, if salt (sodium
chloride) is put into water, it dissolves
and then dissociates into two separate ions
- a positive sodium ion (or cation, Na+),
and a negatively charged chloride ion (or
anion, Cl-). So in solution, sodium chloride
no longer exists and it's ions are free to
move and combine with other ions of an equal
and opposite charge.
Consequently, all ions can
be split into two groups; the positively
charged cations such as calcium, magnesium,
sodium, iron (all metals) and the negatively
charged anions such as bicarbonate,
carbonate, chloride, sulphate, nitrate etc.
Fortunately, the vast
majority of impurities and inconsistencies
between our tap water and that of pure water
are due to an excess of specific ions. And
as these ions will either have a negative or
positive charge, with a little applied
chemistry, we can target and remove these
offending ions using water purifiers.
Next: Dealing with the
dissolved ions.
After the initial filter media
have worked on the raw tap water, there
should only be a significant quantity of
inorganic compounds remaining as ions which
can then be removed using ion exchange
technology.
What is ion
exchange?
Ion exchange is a reversible
chemical process in which the specific ion
(such as sodium, Na+) are released from the
insoluble solid medium (which is the ion
exchange resin) and exchanged for
non-desirable, or target cations, such as
heavy metals. There are two types of ion
exchange that can be caused to occur within
a water purifier; that which removes target
cations and that which removes target
anions.
Ion exchange was first
discovered in 1845 by an Englishman called
Thompson who passed an ammonia-rich solution
of manure through some ordinary garden soil,
only to discover that the ammonia content of
the liquid manure was greatly reduced. It
was later shown that the soil contained fine
particles of a natural material called
zeolite which would even later be shown to
have ion exchange properties. The
water industry has not looked back since,
but developed better and more efficient
media to do the job of water purification.
How cation
exchange works.
Cation exchange resins are
usually made from an inert compound called
polystyrene-divinylbenzene which is heated
in its manufacturing process with
concentrated sulphuric acid, causing a
sulphonic group (SO3-) to be permanently
fixed on to the structural chemistry of the
resin beads. Because these sulphonic groups
have a negative charge, they can be charged
with positively charged ions (cations)
typically sodium (Na+), potassium (K+) or
even hydrogen (H+).
When tap water
containing dissolved cations (such as heavy
metals) pass by the resin, then these are
exchanged for, and trade places with, the
loosely held sodium ions on the resin.
There will come a time when no more cations
can be removed by a fully reacted resin
which is then described as being
'exhausted', and which must then be
replaced.
The better a resin is protected
by pre-filtration from fouling contaminants
such as iron and chlorine (which can
actually cause the resin polymer beads to
disintegrate), the longer it's active life
will be. Cation exchange resins will remove
most metallic, positively charged ions such
as barium, cadmium, copper, iron, manganese,
zinc, calcium and magnesium.
Consequently, if the flow
rate has been sufficiently slow and there
has been sufficient active areas for cation
exchange on the resin, then the levels of
contaminant cations are reduced, and
retained within the resin. All this leaves
is the negatively charged contaminants or
anions which must then be removed.
How anion
exchange works.
Anion exchange units use a
different resin that works in the opposite
way to a cation exchange resin. It is
charged with either chloride (Cl-) or
hydroxyl (OH-) ions, are then released into
the water in exchange for the less desirable
contaminant anions. Anion exchange
removes nitrates, sulphates and other
negatively charged ions.
What is the
difference between absorption and
adsorption?
A sponge absorbs water into
the inside of it's porous structure. Ion
exchange resins are not porous and so we
describe the action by which they attract
and retain ions on to their surface as
adsorption.
There are several new
generation adsorptive media that seek to
replace or improve upon the purifying
performance of activated carbon. Some are
natural media, while others boast patented
technology that enables them to adsorb most
heavy metals and dissolved gases.
Mixed bed
ion exchange.
As the term suggests, these
ion exchange media contain both anionic and
cationic exchange media, combined in one
cartridge. To ensure that there is efficient
purification, mixed bed ion exchange resins
are usually used in a series of multiple
cartridges, preceded as ever, by at least a
carbon filter and at best an additional fine
micron mechanical pre-filter.
In summary, water
purification uses a series of complementary
filtration processes that involve both
mechanical and chemical means to produce
'purified' water. Our tap water can deliver
quite unpredictable levels of ions and other
'contaminants' such as herbicides and
pesticides, as well as chlorine and
chloramine. Different purifiers boast
different qualitative and quantitative
performance figures; a function of the
different types and configurations of media
used in these purifiers. The team of
different media work to target and remove
these contaminants, whether they are present
in our tap water or not. It never ceases to
amaze me that by using the innate
'electrical' features of the dissolved
contaminants themselves, the manufactured
media or resins can effectively remove them
from tap water, with no power or electricity
required to power them.
- Portion of the above excerpt provided by
"The Pond Doctor"
KDF (
Kinetic
Degradation Fluxion)
-
Redox
(more ion exchange)
KDF
is a patented media that is a giant step
forward in water purification.
KDF media utilizes an old process in a new
way - the oxidation and reduction of ions,
known as redox... the principle of
Oxidation-Reduction or Redox potential.
Redox media remove virtually any soluble
heavy metal, help prevent mineral hardness
scale accumulation, and
reduce levels of microorganisms.
Redox reactions,
or oxidation-reduction reactions,
primarily involve the transfer of electrons
between two chemical species. The compound
that loses an electron is said to be
oxidized, the one that gains an electron is
said to be reduced.
KDF process
media are high-purity copper-zinc granules
used in a number of pretreatment, primary
treatment and wastewater treatment
applications. KDF media supplement or
replace existing technologies to
dramatically extend life of the system,
control heavy metals, toxic gases and
microorganisms, lower total cost, and
decrease maintenance. KDF process media work
to reduce or remove chlorine, iron, hydrogen
sulfide, lead, mercury, calcium carbonate,
magnesium, chromium, bacteria, algae, fungi,
and much more!
Iron and hydrogen sulfide are oxidized into
insoluable matter and attach to the surface
of the media. Heavy metals such as
lead, mercury, iron, cadmium and aluminum
are removed from the water by the
electrochemical process. They are attracted
to the surface of the media, much like a
magnet.
In short, the redox process works by
exchanging electrons with contaminants. This
give and take of electrons converts many
harmful contaminants into harmless
components, such as chlorine to chloride.
Other contaminants, including heavy metals,
bond to the KDF media, which greatly reduces
or virtually eliminates these substances.
The media also inhibits bacteria, algae, and
fungi growth. KDF process media control microorganisms in
two ways. The first is a by-product of redox;
the exchange of electrons sets up an
electrolytic field in which most microorganisms
cannot survive. Secondly, the process of forming
hydroxyl radicals and peroxides from some of the
water molecules interferes with the
microorganisms' ability to function.
Ozone is a GREAT way to
purify your water. Ozone (O3) is
the triatomic form of oxygen
(O2). It is oxygen in it's most
active state and is an extremely
potent oxidant that has been
shown to posses broad spectrum
antimicrobial activity. Ozone is
not just another disinfectant.
Ozone is a true sterilant. It
has the ability to completely
destroy not only bacteria, but
also viruses, spores, fungus,
mold, mildew, cysts, and many
other contaminants while at the
same time breaking down
dissolved organic materials by
oxidation. When ozone (O3)
breaks down it naturally reverts
back to oxygen (O2).
Both the FDA and EPA certify
that
ozone destroys 99.9992% of all
pathogenic germs, while oxidizing (destroying)
99.9992% nearly ALL other pollutants in the water
at the same time.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis of water
is the decomposition of
water (H2O)
into oxygen (O)
and hydrogen gas (H2)
due to an electric
current being passed
through the water. This
electrolytic process is
used in some industrial
applications when
hydrogen is needed.
An
electrical power source
is connected to two
electrodes, or two
plates, (typically made
from some inert metal
such as platinum or
stainless steel) which
are placed in the water.
Hydrogen will appear at
the cathode (the
negatively charged
electrode, where
electrons are pumped
into the water), and
oxygen will appear at
the anode (the
positively charged
electrode). The
generated amount of
hydrogen is twice the
amount of oxygen, and
both are proportional to
the total electrical
charge that was sent
through the water.
During this
process, H+
cations will
accumulate at the anode
and OH−
anions will
accumulate at the
cathode. This can be
verified by adding a
pH indicator to the
water: the water near
the anode is acidic
while the water near the
cathode is basic.
see our electrolyses
machines here
Magnetic Fields
and Water
A water molecule. |
At
first site, water seems
to be a very simple molecule, consisting of just
two hydrogen atoms attached to an oxygen atom.
Indeed, there are very few molecules that are
smaller or lighter.
Once a water molecule has been exposed to a
magnetic field the molecule changes in several
ways:
1. The molecule increases in
size. This increases the water solubility
and permeability (the ability to disperse
and penetrate other substances). The
increase in permeability assists in the
dissolution of
nutritional
substances, and improves the body's
absorption of water as well as the
nutritional substances. Also, when the size
of the water molecule is increased its
ability to absorb toxins is much greater.
2. The surface tension and density of the
water is increased. The increased surface
tension, permeability, and density all
combine to improve the intake of
nutrition
in the body's cell structure. Increased
surface tension allows the cell membrane of
the food to expand rapidly. This is
beneficial to digestion. The increase in
density also aids in the absorption of
nutrition.
3. The ions in the water are affected.
This
has the effect of reducing free radicals
contained within the water (free radicals
are harmful substances found in the body). A
further benefit of the alteration to the ion
states of both calcium carbonate and
magnesium carbonate is this: the structure
of these compounds (which are the cause of
the scale build up in water pipes, kettles,
taps, etc) changes, resulting in a much
decreased build up of scale due to the
looser nature of the ions. (SOFT WATER) This decrease in
scale build up has resulted in extensive use
of magnetized water in central heating
systems, water cooling systems in engines,
recycling
water systems, and
house water systems.
Read more
about magnets and water here
We've
reviewed dozens of filters and filter
combinations for years. As a Holistic
Health Practitioner, we seek to offer only the
very best quality we can find. Clean water is
paramount to good health. We are proud to
offer the top of the line Wholly Water Drinking
Water System.

 |
| |
|
 |
Removes
the BROADEST RANGE of
Toxins! |
 |
NO filter
media changes or repacking!
|
 |
Lasts up to
15
YEARS or longer! |
 |
Patented System |
The
Wholly Water Purification System Includes the Following:
- 6-Bed, 5 STAGE
Patented Water Filter
-
Dedicated Long-reach Faucet
- Pressure
Regulator - 3/8 inch
- Sonic Flood Alarm
- Easy
Instructions
-
2 year warranty
-
Can split to feed Icemaker/Frig water
dispenser
Chlorine - ALL Heavy Metals
- PCB's -
Organic & Inorganic - VOC's
Radionuclides - Bacteria -
Cysts - MTBE -
Pharmaceuticals
Better than bottled water. Better than R/O. Better than any other filter!
 |
Our water supply is arguably the
single most contributory
factor in today's epidemic
of skyrocketing immune disorders
and other diseases. This is the
most affordable and comprehensive under-counter
drinking water filter we've ever
seen! The
whole
house water filter
is equally effective.